The main reason that nulls aren't allowed in ConcurrentMaps
(ConcurrentHashMaps, ConcurrentSkipListMaps) is that
ambiguities that may be just barely tolerable in non-concurrent
maps can't be accommodated. The main one is that if
map.get(key) returns null, you can't detect whether the
key explicitly maps to null vs the key isn't mapped.
In a non-concurrent map, you can check this via map.contains(key),
but in a concurrent one, the map might have changed between calls.
Further digressing: I personally think that allowing
nulls in Maps (also Sets) is an open invitation for programs
to contain errors that remain undetected until
they break at just the wrong time. (Whether to allow nulls even
in non-concurrent Maps/Sets is one of the few design issues surrounding
Collections that Josh Bloch and I have long disagreed about.)
>
> It is very difficult to check for null keys and values
> in my entire application .
>
Would it be easier to declare somewhere
static final Object NULL = new Object();
and replace all use of nulls in uses of maps with NULL?
---- Doug Lea
基本结构
Java 8 之前的结构
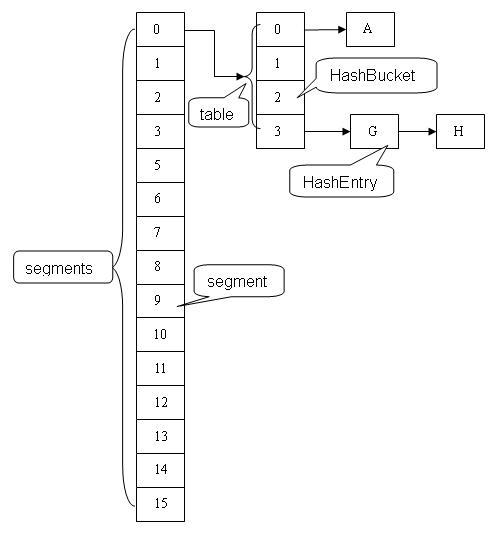
HashEntry
static final class HashEntry<K,V> {
final K key; // 声明 key 为 final 型
final int hash; // 声明 hash 值为 final 型
volatile V value; // 声明 value 为 volatile 型
final HashEntry<K,V> next; // 声明 next 为 final 型
HashEntry(K key, int hash, HashEntry<K,V> next, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.hash = hash;
this.next = next;
this.value = value;
}
}
Segment:
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
/**
* 在本 segment 范围内,包含的 HashEntry 元素的个数
* 该变量被声明为 volatile 型
*/
transient volatile int count;
/**
* table 被更新的次数, 每次更新操作如put、remove等都会对modCount加一。
*/
transient int modCount;
/**
* 当 table 中包含的 HashEntry 元素的个数超过本变量值时,触发 table 的再散列
*/
transient int threshold;
/**
* table 是由 HashEntry 对象组成的数组
* 如果散列时发生碰撞,碰撞的 HashEntry 对象就以链表的形式链接成一个链表
* table 数组的数组成员代表散列映射表的一个桶
* 每个 table 守护整个 ConcurrentHashMap 包含桶总数的一部分
* 如果并发级别为 16,table 则守护 ConcurrentHashMap 包含的桶总数的 1/16
*/
transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table;
/**
* 装载因子
*/
final float loadFactor;
Segment(int initialCapacity, float lf) {
loadFactor = lf;
setTable(HashEntry.<K,V>newArray(initialCapacity));
}
/**
* 设置 table 引用到这个新生成的 HashEntry 数组
* 只能在持有锁或构造函数中调用本方法
*/
void setTable(HashEntry<K,V>[] newTable) {
// 计算临界阀值为新数组的长度与装载因子的乘积
threshold = (int)(newTable.length * loadFactor);
table = newTable;
}
/**
* 根据 key 的散列值,找到 table 中对应的那个桶(table 数组的某个数组成员)
*/
HashEntry<K,V> getFirst(int hash) {
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
// 把散列值与 table 数组长度减 1 的值相“与”,
// 得到散列值对应的 table 数组的下标
// 然后返回 table 数组中此下标对应的 HashEntry 元素
return tab[hash & (tab.length - 1)];
}
}
put操作
- 和HashMap一样计算hash值。
- 根据hash值计算segment对象位置。
- 在segment的table中执行put方法。
注意点:
- Segment是一个可重入锁,put会首先对segment加锁。
- 这里的加锁操作是针对(键的 hash 值对应的)某个具体的 Segment,锁定的是该 Segment 而不是整个 ConcurrentHashMap。
- rehash不再针对整个map,而是segment中的table数组。
- 使用头插法在链表中添加新的节点。
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (value == null) //ConcurrentHashMap 中不允许用 null 作为映射值
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); // 计算键对应的散列码
// 根据散列码找到对应的 Segment
return segmentFor(hash).put(key, hash, value, false);
}
/**
* 使用 key 的散列码来得到 segments 数组中对应的 Segment
*/
final Segment<K,V> segmentFor(int hash) {
// 将散列值右移 segmentShift 个位,并在高位填充 0
// 然后把得到的值与 segmentMask 相“与”
// 从而得到 hash 值对应的 segments 数组的下标值
// 最后根据下标值返回散列码对应的 Segment 对象
return segments[(hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask];
}
V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
lock(); // 加锁,这里是锁定某个 Segment 对象而非整个 ConcurrentHashMap
try {
int c = count;
if (c++ > threshold) // 如果超过再散列的阈值
rehash(); // 执行再散列,table 数组的长度将扩充一倍。
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
// 把散列码值与 table 数组的长度减 1 的值相“与”
// 得到该散列码对应的 table 数组的下标值
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
// 找到散列码对应的具体的那个桶
HashEntry<K,V> first = tab[index];
HashEntry<K,V> e = first;
while (e != null && (e.hash != hash || !key.equals(e.key)))
e = e.next;
V oldValue;
if (e != null) { // 如果键值对存在
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.value = value; // 设置 value 值
}
else { // 键值对不存在
oldValue = null;
++modCount; // 要添加新节点到链表中,所以 modCont 要加 1
// 创建新节点,并添加到链表的头部
tab[index] = new HashEntry<K,V>(key, hash, first, value);
count = c; // 写 count 变量
}
return oldValue;
} finally {
unlock(); // 解锁
}
}
get操作
V get(Object key, int hash) {
if (count != 0) { // read-volatile, count也是volatile。
HashEntry<K,V> e = getFirst(hash);
while (e != null) {
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {
V v = e.value;
if (v != null)
return v;
return readValueUnderLock(e); // recheck
}
e = e.next;
}
}
return null;
}
ConcurrentHashMap的读操作除特殊情况外,除特殊情况外,并不需要对segment进行加锁。从HashEntry的结构可以看到:
static final class HashEntry<K,V> {
final K key; // 声明 key 为 final 型
final int hash; // 声明 hash 值为 final 型
volatile V value; // 声明 value 为 volatile 型
final HashEntry<K,V> next; // 声明 next 为 final 型
除了value为volatile外,key、hash、next都为final不能改变。
- 对于只改变value值的操作,由于value为volatile修饰,读线程能够保证读到最新的值。
- ==对于改变map结构的操作,如put添加新元素、remove删除元素、clear清除map中所有的值。==
- put操作,由于next为final,因此只能在链表头添加新元素,不影响正在遍历链表的读线程。
- remove操作,==由于无法修改next域,因此remove操作需要复制被删元素的所有前元素,并将前元素链接至被删除元素后一个元素==。
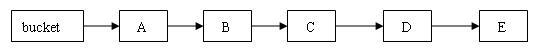
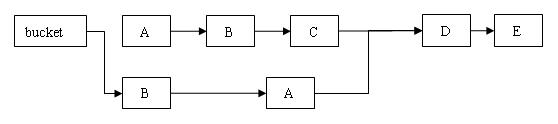
- clear操作,只是将segment中table的元素置空,不再链接至原链表,仍在原链表上遍历的读线程不受影响。
- get操作首先会读segment count域得到segment中的元素个数,而count域也是一个volatile修饰的域,并且所有的写操作最后都会更新count域。因此读线程也能保证在开始读的时候得到的是最新的map结构。
- 当读到value值为null时,会调用readValueUnderLock方法,对segment加锁后再读取。因此读操作并不是完全不会加锁的。
V readValueUnderLock(HashEntry<K,V> e) { lock(); try { return e.value; } finally { unlock(); } }ConcurrentHashMap不允许key和value值为null,之所有读操作可能读到空值,是因为在put操作中有:
tab[index] = new HashEntry<K,V>(key, hash, first, value)其中HashEntry构造函数中对value的赋值以及对tab[index]的赋值可能被重新排序,也就是先对tab[index]赋值,再对value赋值,这就可能导致结点的值为空。
跨段操作
SIZE
public int size() {
final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments;
long sum = 0;
long check = 0;
int[] mc = new int[segments.length];
// Try a few times to get accurate count. On failure due to
// continuous async changes in table, resort to locking.
for (int k = 0; k < RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK; ++k) {
check = 0;
sum = 0;
int mcsum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) {
sum += segments[i].count;
mcsum += mc[i] = segments[i].modCount;
}
if (mcsum != 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) {
check += segments[i].count;
if (mc[i] != segments[i].modCount) {
check = -1; // force retry
break;
}
}
}
if (check == sum)
break;
}
if (check != sum) { // Resort to locking all segments
sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i)
segments[i].lock();
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i)
sum += segments[i].count;
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i)
segments[i].unlock();
}
if (sum > Integer.MAX_VALUE)
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
else
return (int)sum;
}
size操作首先在不加锁的情况下遍历所有的segments,尝试RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK次,每次遍历两遍,如果这两遍得到的count总值sum相同,并且每一个segment的modCount都没有发生变化,就返回sum的值。
如果尝试RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK次后仍然不能得到sum的值,那么对所有的segment加锁后,再计算sum的值。
本文地址:https://cheng-dp.github.io/2018/08/26/concurrentHashMap-before-java8/