使用案例
class RWDictionary {
private final Map<String, Data> m = new TreeMap<String, Data>();
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
private final Lock r = rwl.readLock();
private final Lock w = rwl.writeLock();
public Data get(String key) {
r.lock();
try { return m.get(key); }
finally { r.unlock(); }
}
public String[] allKeys() {
r.lock();
try { return m.keySet().toArray(); }
finally { r.unlock(); }
}
public Data put(String key, Data value) {
w.lock();
try { return m.put(key, value); }
finally { w.unlock(); }
}
public void clear() {
w.lock();
try { m.clear(); }
finally { w.unlock(); }
}
}
实现特点
ReentrantReadWriteLock和其他JUC同步工具类一样,定义了Sync类继承自AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,并且有FairSync和NonfairSync两个子类继承Sync支持公平模式和非公平模式。
ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock是共享锁,ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock是独占锁,ReadLock和WriteLock包含同一个Sync实现,为了同时支持共享模式和独占模式:
-
共享状态int state记录读锁和写锁的重入次数。低16位记录写锁重入次数,高16位记录读锁重入次数。
-
Sync类中同时实现了AQS的独占模式方法(tryAcquire/tryRelease)和共享模式方法(tryAcquireShared/tryReleaseShared)。
-
使用同一个等待队列维护读/写线程,读线程Node为SHARED共享模式,写线程Node为Exclusive模式。
-
写线程加锁和解锁利用tryAcquire()和tryRelease()方法,读线程加锁和解锁利用tryAcquireShared()和tryReleaseShared()方法。
-
tryAcquire()/tryRelease()/tryAcquireShared()/tryReleaseShared()的返回值,都是根据当前int state记录的读锁和写锁重入次数,依据读写锁定义决定的。
-
state中只记录了读锁总共被重入的次数。每个线程自身重入读锁的次数记录在该线程的ThreadLocal中。getReadHoldCount()返回该值。(getWriteHoldCount()直接返回state中记录的写锁重入次数)。
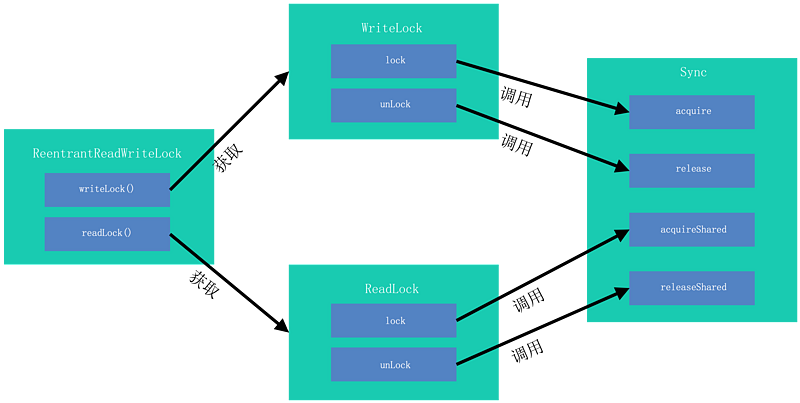
实现分析
写锁
写锁为独占锁,AQS子类Sync重写tryAcquire(int acquires)。
- 当有读锁或者有写锁但不是该线程持有时,返回false。
- 如果写锁重入次数超过65535(16位),抛出ERROR。
- 否则根据Fair和NonFair规则尝试获取锁。
- tryAcquire返回false时AQS中会调用acquireQueue进行排队。
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { //acquires = 1 in lock
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If read count nonzero or write count nonzero
* and owner is a different thread, fail.
* 2. If count would saturate, fail. (This can only
* happen if count is already nonzero.)
* 3. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for lock if
* it is either a reentrant acquire or
* queue policy allows it. If so, update state
* and set owner.
*/
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
int w = exclusiveCount(c);
if (c != 0) {
// (Note: if c != 0 and w == 0 then shared count != 0)
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
return false;
if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
// Reentrant acquire
setState(c + acquires);
return true;
}
if (writerShouldBlock() ||
!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires))
return false;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
//writerShouldBlock in FairSync:
final boolean writerShouldBlock() {
return hasQueuedPredecessors();
}
//writerShouldBlock in NonfairSync:
final boolean writerShouldBlock() {
return false; // writers can always barge
}
释放锁,AQS子类Sync重写tryRelease(int releases)。
- state的exclusive部分减去release数目,结果为0则返回true。
- tryRelease返回true时,AQS release方法会调用unparkSuccessor释放后继节点线程,如果是读线程,状态为SHARED,释放会被传导至其后连续的所有读线程。
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {//releases = 1 in unlock
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
int nextc = getState() - releases;
boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;
if (free)
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(nextc);
return free;
}
读锁
读锁为共享模式,同时可以有多个线程占有读锁。
- state的高16位记录读锁被占有和重入的总数。
- 每个线程中ThreadLocalHoldCounter记录该线程重入读锁的数目。
获取锁,AQS子类Sync重写tryAcquireShared(int acquires)。
- 如果写锁被占有,且不是本线程占有写锁,返回-1。(获取了写锁的线程可以再获取读锁,详见锁降级)。
- 根据公平规则判断是否要排队等待readerShouldBlock()。
- CAS尝试更新state。如果成功:
- 如果读锁计数为0,更新firstReader,firstReaderHoldCount。
- 如果读锁计数不为0,该线程是第一个获取读锁的线程,更新firstReaderHoldCount++。
- 如果该线程不是第一个获取读锁的线程,更新ThreadLocal的重入计数。
- CAS更新失败,或需要排队,调用fullTryAcquireShared(current)在循环中反复抢占读锁。
```java
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
/*
- Walkthrough:
-
- If write lock held by another thread, fail.
-
- Otherwise, this thread is eligible for
- lock wrt state, so ask if it should block
- because of queue policy. If not, try
- to grant by CASing state and updating count.
- Note that step does not check for reentrant
- acquires, which is postponed to full version
- to avoid having to check hold count in
- the more typical non-reentrant case.
-
- If step 2 fails either because thread
- apparently not eligible or CAS fails or count
- saturated, chain to version with full retry loop. */ Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 && getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current) return -1; int r = sharedCount(c); if (!readerShouldBlock() && r < MAX_COUNT && compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) { if (r == 0) { firstReader = current; firstReaderHoldCount = 1; } else if (firstReader == current) { firstReaderHoldCount++; } else { HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter; if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get(); else if (rh.count == 0) readHolds.set(rh); rh.count++; } return 1; } return fullTryAcquireShared(current); } ```
释放锁,AQS子类Sync重写tryReleaseShared(int acquires)。
- 计算并更新firstReaderHoldCount, readHolds的值。
- 计算state的值,在for循环中CAS更新,如果为0,此时读锁和写锁都没有被持有,返回true,否则返回false。
- AQS releaseShared中,当tryReleaseShared返回true时,调用doReleaseShared释放等待队列中下一个线程(为写线程)。
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
if (firstReader == current) {
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
if (firstReaderHoldCount == 1)
firstReader = null;
else
firstReaderHoldCount--;
} else {
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
int count = rh.count;
if (count <= 1) {
readHolds.remove();
if (count <= 0)
throw unmatchedUnlockException();
}
--rh.count;
}
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
// Releasing the read lock has no effect on readers,
// but it may allow waiting writers to proceed if
// both read and write locks are now free.
return nextc == 0;
}
}
锁降级
在线程已经获取写锁的情况下,可以继续获取读锁,此时其他线程仍然无法获取读锁或写锁。线程释放写锁后,会唤醒后续等待节点,且后续节点可见的状态为该线程获取了读锁。也就是写锁可以降级为读锁。
//锁降级的应用场景
class CachedData {
Object data;
volatile boolean cacheValid;
final ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
void processCachedData() {
rwl.readLock().lock();
if (!cacheValid) {
// Must release read lock before acquiring write lock
rwl.readLock().unlock();
rwl.writeLock().lock();
try {
// Recheck state because another thread might have
// acquired write lock and changed state before we did.
if (!cacheValid) {
data = ...
cacheValid = true;
}
// Downgrade by acquiring read lock before releasing write lock
rwl.readLock().lock();
} finally {
rwl.writeLock().unlock(); // Unlock write, still hold read
}
}
try {
use(data);
} finally {
rwl.readLock().unlock();
}
}
}
在上面的例子中,当cacheValid为false时,首先写加锁,写入数据使得cacheValid为true,再降级为读锁处理数据。其中(加写锁、修改值、加读锁、释放写锁、使用数据、释放读锁)为典型的锁降级。
如果不使用锁降级,则过程可能有两种情况:
1.(加写锁、修改值、使用数据、释放写锁), 不释放写锁,直接在写锁状态下使用数据,读取操作阻塞了其他读线程,变成了排它锁。
- (加写锁、修改值、释放写锁、加读锁、使用数据、释放读锁),释放写锁和获取读锁存在时间差,可能造成当前线程进入等待队列,降低吞吐量。
为什么不能有锁升级(读锁变写锁):
- 多个读锁的情况下,某个读锁升级为写锁,此时同时有读锁和写锁,和读写锁的定义不符。
- 读锁再申请写锁,需要等待读锁释放才能获取写锁,死锁。
REFS
- https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000015768003
- https://blog.csdn.net/fuyuwei2015/article/details/72597192
- https://blog.csdn.net/patrickyoung6625/article/details/44960371
本文地址:https://cheng-dp.github.io/2018/11/15/reentrant-read-write-lock/