- 简单工厂模式
- 工厂方法模式
- 单例模式
- 代理模式
- 适配器模式
- 装饰器模式
- 观察者模式
- 策略模式
- 模板方法模式
简答工厂模式(SimpleFactoryPattern)
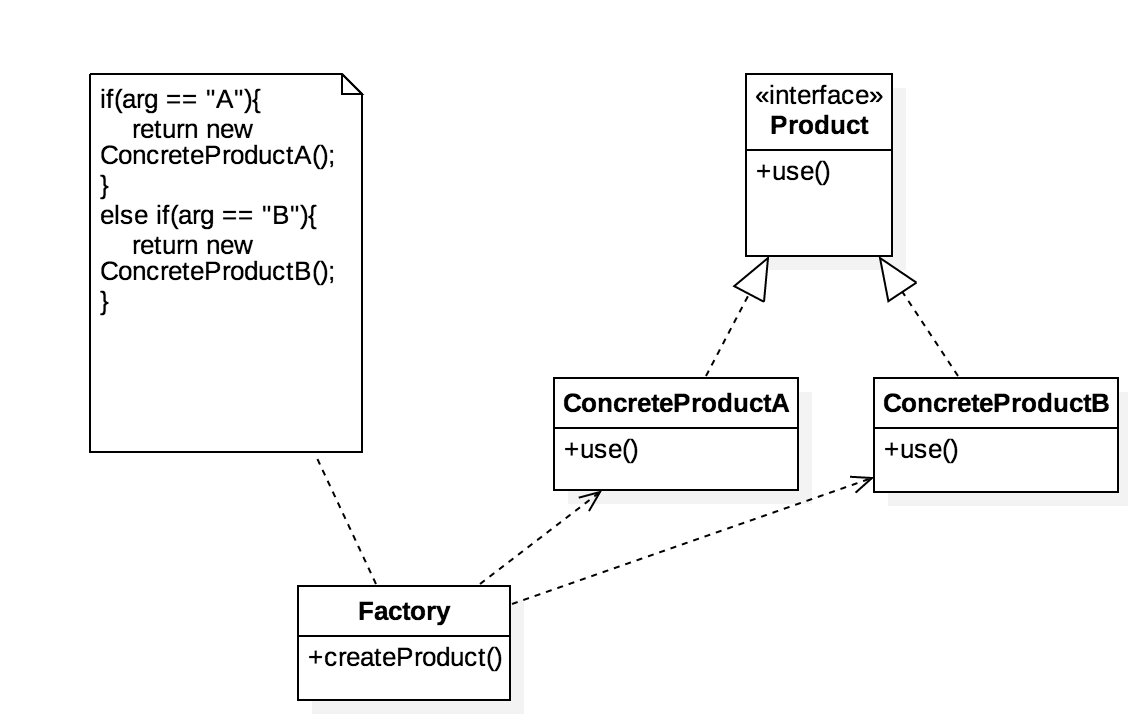
Spring中的应用
BeanFactory.getBean("beanName");,根据给定的beanName构造并返回bean实例。
工厂方法模式(FactoryMethodPattern)
简单工厂模式,不符合开闭原则,如果要增加新的产品,需要修改工厂类源代码。为了解决这个问题,在工厂方法模式中,父类负责定义创建对象的公共接口,而子类则负责生成具体的对象,这样做的目的是将类的实例化操作延迟到子类中完成,即由子类来决定究竟应该实例化(创建)哪一个类。
对于产品的改动,只需要增加、减少、修改具体的子类工厂。
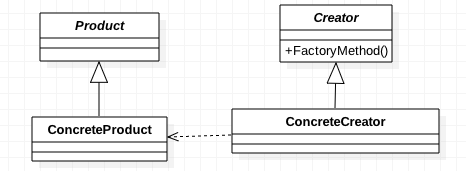
Spring中的应用
FactoryBean
Spring中有两种类型的Bean,一种是普通Bean,另一种是FactoryBean。FactoryBean返回的对象不是指定类的一个实例,而是该工厂Bean的getObject方法所返回的对象。
一个FactoryBean就是工厂方法模式中的一个具体工厂。
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
public interface FactoryBean<T> {
@Nullable
T getObject() throws Exception;
@Nullable
Class<?> getObjectType();
default boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
单例模式(SingletonPattern)
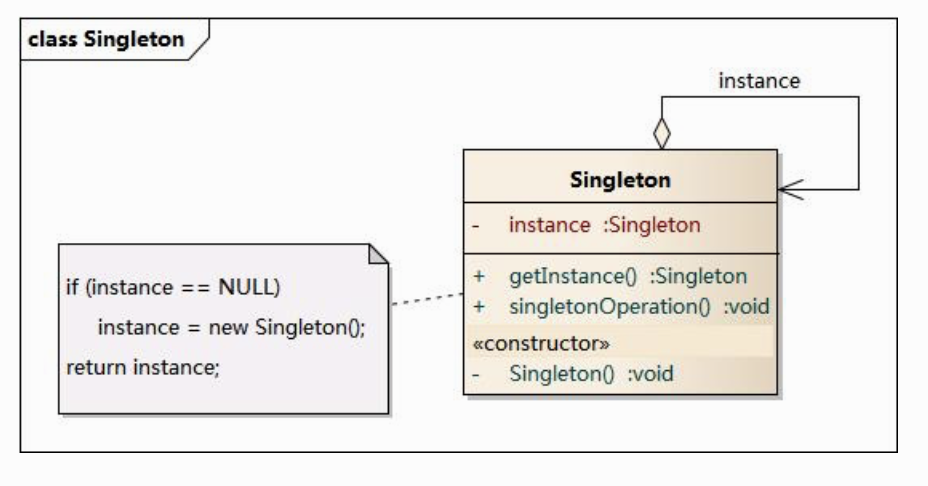
单例模式确保某一个类只有一个实例,而且自行实例化并向整个系统提供这个实例,这个类称为单例类,它提供全局访问的方法。
Spring中的应用
Singleton Bean,在ApplicationContext容器创建时,会实例化所有的Singleton bean。
代理模式(ProxyPattern)
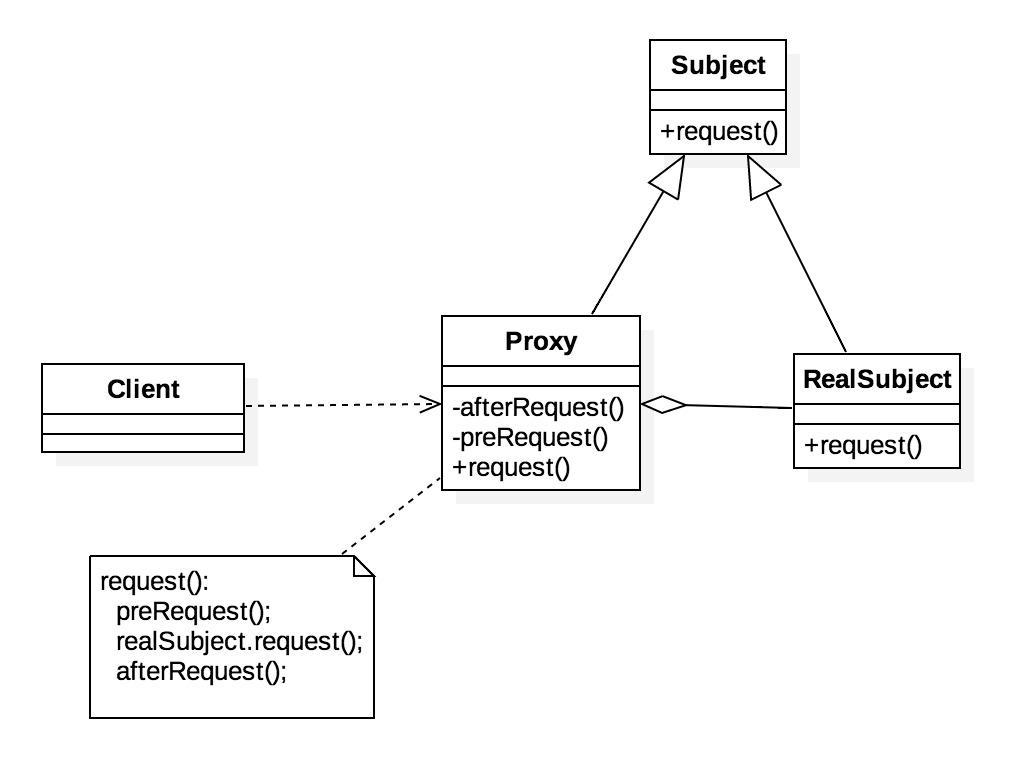
代理对象可以在客户端和目标对象之间起到中介的作用,并且可以通过代理对象去掉客户不能看到的内容和服务或者添加客户需要的额外服务。
Spring中的应用
Spring中AOP的实现基础就是通过JDK动态代理 和 cglib动态代理 方法为Bean创建代理。
适配器模式(Adapter/Wrapper Pattern)
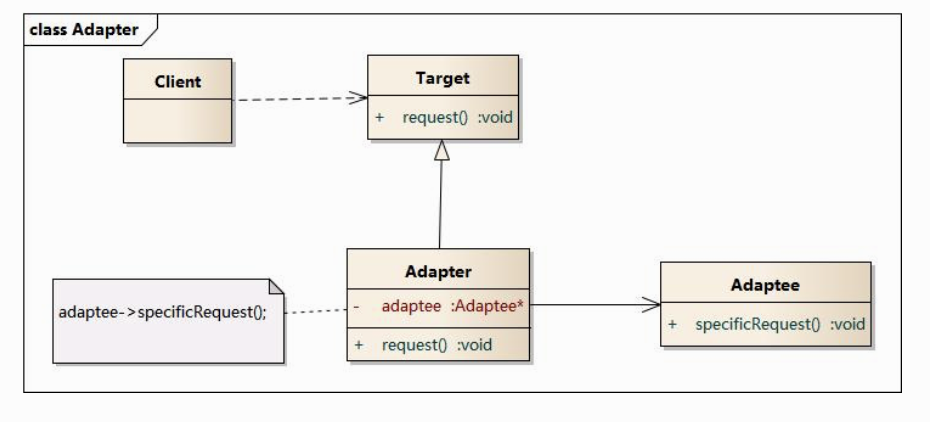
将一个接口转换成客户希望的另一个接口,适配器模式使接口不兼容的那些类可以一起工作,其别名为包装器(Wrapper)。 被包装的类或接口称为Adaptee(适配者类)。
Spring中的应用
在Spring AOP中,使用Advice来增强被代理类的功能。Spring通过创建Bean的代理类的方式实现AOP,并在代理类中、被代理类的方法执行前,设置拦截器(Interceptor),执行Advice。因此,为了执行Advice方法,需要为Advice创建适配器,将Advice转换为Interceptor。
public interface AdvisorAdapter {
boolean supportsAdvice(Advice advice);
MethodInterceptor getInterceptor(Advisor advisor);
} MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter类,Adapter
class MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter implements AdvisorAdapter, Serializable {
public boolean supportsAdvice(Advice advice) {
return (advice instanceof MethodBeforeAdvice);
}
public MethodInterceptor getInterceptor(Advisor advisor) {
MethodBeforeAdvice advice = (MethodBeforeAdvice) advisor.getAdvice();
return new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(advice);
}
}
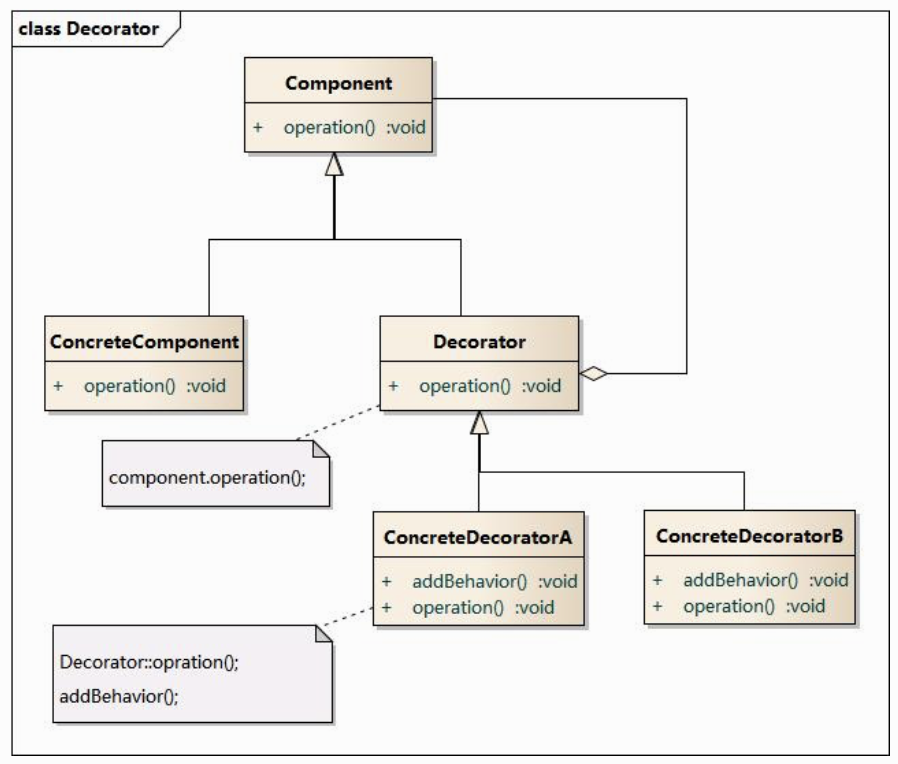
装饰器模式(Decorator/Wrapper Pattern)
装饰器与适配器都有一个别名叫做包装模式(Wrapper),它们看似都是起到包装一个类或对象的作用,但是使用它们的目的很不一样。适配器模式的意义是要将一个接口转变成另一个接口,它的目的是通过改变接口来达到重复使用的目的。
而装饰器模式不是要改变被装饰对象的接口,而是恰恰要保持原有的接口,但是增强原有对象的功能,或者改变原有对象的处理方式而提升性能。所以这两个模式设计的目的是不同的。
保持原有的接口,但是增强原有对象的功能,或者改变原有对象的处理方式而提升性能。
Decorator是一个继承Component的接口或者抽象类,加入了新功能方法,由ConcreteDecorator完成新功能实现。
Spring中的应用
BeanDefinitionDecorator:
/**
* Interface used by the {@link DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader}
* to handle custom, nested (directly under a {@code <bean>}) tags.
*/
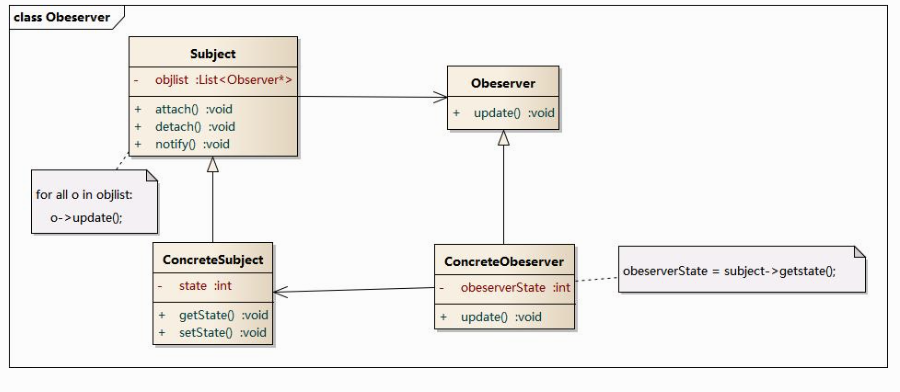
观察者模式(ObserverPattern/public-subscriber/listener pattern)
建立一种对象与对象之间的依赖关系,一个对象发生改变时将自动通知其他对象,其他对象将相应做出反应。
观察者模式又叫 发布-订阅模式(public-subscriber/listener)。
Spring中的应用
ApplicationListener:
/**
* Interface to be implemented by application event listeners.
* Based on the standard {@code java.util.EventListener} interface
* for the Observer design pattern.
*
* <p>As of Spring 3.0, an ApplicationListener can generically declare the event type
* that it is interested in. When registered with a Spring ApplicationContext, events
* will be filtered accordingly, with the listener getting invoked for matching event
* objects only.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @param <E> the specific ApplicationEvent subclass to listen to
* @see org.springframework.context.event.ApplicationEventMulticaster
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {
/**
* Handle an application event.
* @param event the event to respond to
*/
void onApplicationEvent(E event);
}
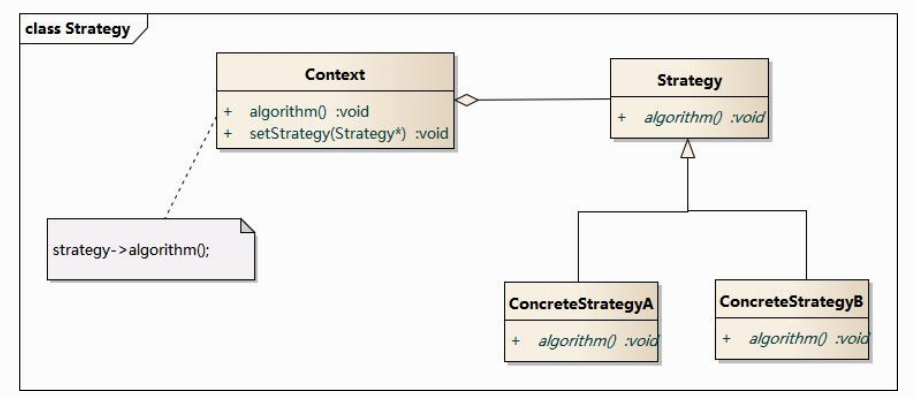
策略模式(StrategyPattern)
定义一系列算法,将每一个算法封装起来,并让它们可以相互替换。策略模式让算法独立于使用它的客户而变化。
Spring中的应用
BeanPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor
模板方法模式(TemplateMethodPattern)
模板方法模式在一个方法中定义一个算法的骨架,而将一些步骤的实现延迟到子类中。模板方法使得子类可以在不改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义算法中某些步骤的具体实现。
Spring中的应用
ConfigurableApplicationContext接口定义了模板方法refresh(),AbstractApplicationContext继承了ConfigurableApplicationContext并实现了refresh()方法,该方法是IoC容器初始化的入口。
在refresh()方法中,定义了若干方法留给子类实现,及模板方法模式的钩子方法:
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for registering special
* BeanPostProcessors etc in certain ApplicationContext implementations.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
*/
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
}
/**
* Template method which can be overridden to add context-specific refresh work.
* Called on initialization of special beans, before instantiation of singletons.
* <p>This implementation is empty.
* @throws BeansException in case of errors
* @see #refresh()
*/
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
- https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-spring-principle/index.html
- http://www.javabench.in/2012/02/design-patterns-being-used-in-spring.html
- https://www.javainuse.com/spring/spring-design-patterns
- https://blog.eduonix.com/java-programming-2/learn-design-patterns-used-spring-framework/
FactoryPattern
- https://blog.csdn.net/hanruikai/article/details/81975948
Adapter/Wrapper
- https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-adapter-pattern/index.html
- http://www.cnblogs.com/brucemengbm/p/6691482.html
TemplatePattern
- https://blog.csdn.net/z69183787/article/details/65628166
本文地址:https://cheng-dp.github.io/2019/03/04/design-pattern-in-spring/