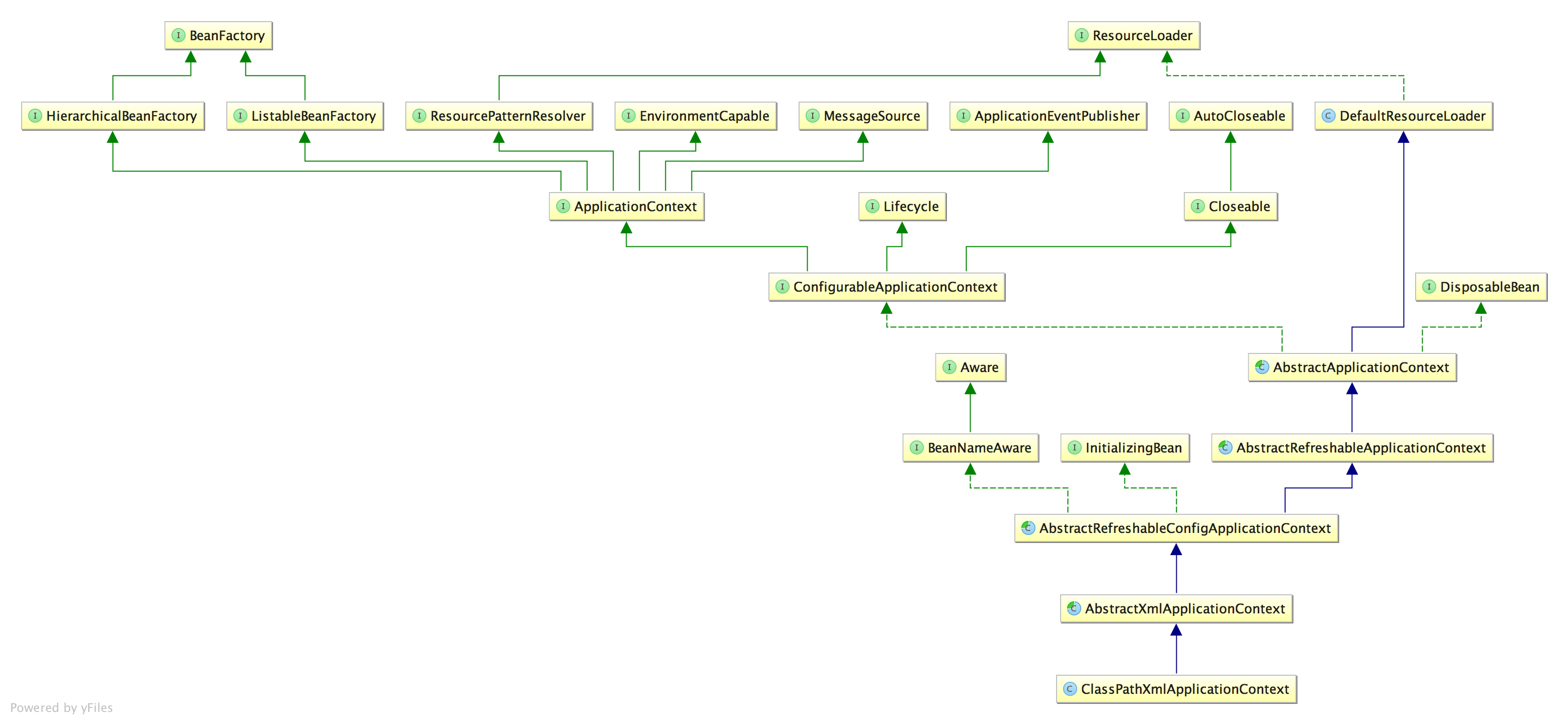
ApplicationContext接口
/**
* Central interface to provide configuration for an application.
* This is read-only while the application is running, but may be
* reloaded if the implementation supports this.
*
* <p>An ApplicationContext provides:
* <ul>
* <li>Bean factory methods for accessing application components.
* Inherited from {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory}.
* <li>The ability to load file resources in a generic fashion.
* Inherited from the {@link org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader} interface.
* <li>The ability to publish events to registered listeners.
* Inherited from the {@link ApplicationEventPublisher} interface.
* <li>The ability to resolve messages, supporting internationalization.
* Inherited from the {@link MessageSource} interface.
* <li>Inheritance from a parent context. Definitions in a descendant context
* will always take priority. This means, for example, that a single parent
* context can be used by an entire web application, while each servlet has
* its own child context that is independent of that of any other servlet.
* </ul>
*
* <p>In addition to standard {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory}
* lifecycle capabilities, ApplicationContext implementations detect and invoke
* {@link ApplicationContextAware} beans as well as {@link ResourceLoaderAware},
* {@link ApplicationEventPublisherAware} and {@link MessageSourceAware} beans.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory
* @see org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader
*/
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory, MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
String getId();
String getApplicationName();
String getDisplayName();
long getStartupDate();
ApplicationContext getParent();
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
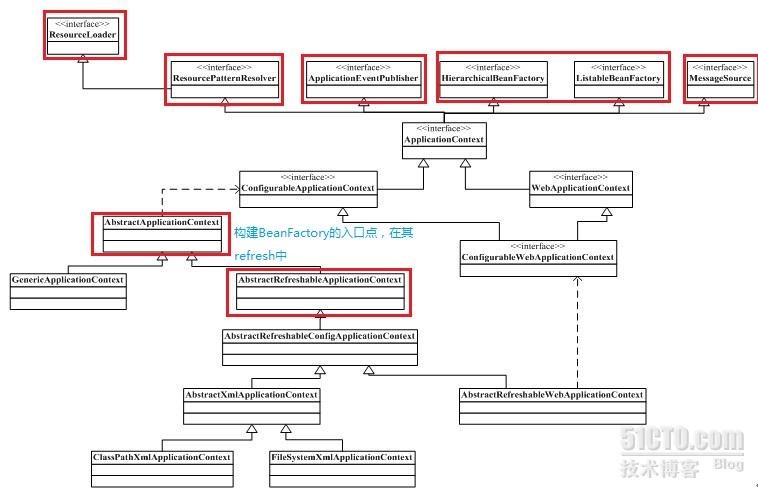
ApplicationContext除了继承了BeanFactory支持IoC容器的基本功能外,还扩展了其他特性:
- MessageSource,支持多消息源,主要用于主要用于国际化。
- ApplicationEventPublisher,支持事件发布,与Spring的生命周期相结合,更好地管理和扩展Spring。
- ResourcePatternResolver,基类为ResourceLoader,支持资源模式,更好地对各种方式(文件或I/O)定义的资源文件的处理。
- EnvironmentCapable,对环境的感知。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的IoC实现
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext是ApplicationContext两个重要实现。
初始化
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
setConfigLocations(configLocations)
setConfigLocations方法将构造方法传入的资源文件设置到AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext的configLocations集合中。
refresh()
refresh()方法是初始化的核心,实现在AbstractApplicationContext中。在refresh方法中,Spring抽象出每个细分操作为单独的方法,然后按顺序进行调用。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 刷新前准备,主要是设置开始时间以及标识active标志位为true
prepareRefresh();
// 从配置中加载BeanDefinition, 创建BeanFactory实例
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// BeanFactory准备工作
// 1. 设置加载Bean用的ClassLoader,解析Bean定义表达式的表达式解析器,读取BeanDefinition的属性编辑注册器。
// 2. 添加ApplicationContextAwareProcessor这个BeanPostProcessor。
// 3. 设置特殊的Bean,BeanFactory, ResourceLoader, ApplicationEventPublisher, ApplicationContext。
// 4. 设置环境变量。
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 在BeanFactory创建完成后,交给子类实现的一个扩展点,如web项目中配置ServletContext
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 实例化并执行所有注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 实例化并注册所有BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 初始化消息源
initMessageSource();
// 初始化上下文事件机制
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 为特殊的上下文预留的方法,初始化特殊的bean
onRefresh();
// 注册监听器
registerListeners();
// 冻结所有配置并实例化所有非lazy-init的单例bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 初始化生命周期,发布容器事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt", ex);
// 销毁已经创建的单例bean
destroyBeans();
// 重置active标识
cancelRefresh(ex);
throw ex;
}
}
}
BeanFactory的创建和准备
BeanFactory的创建和准备由前两个方法共同完成:
-
obtainFreshBeanFactory()
==完成BeanDefinition的载入、注册==,最终返回DefaultListableBeanFactory。
-
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)
创建好beanFactory后,添加Spring本身需要的工具类。为容器配备了ClassLoader,PropertyEditor和BeanPostProcessor。
obtainFreshBeanFactory
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
refreshBeanFactory()方法在AbstractApplicationContext的子类AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中定义:
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
// 如果已存在BeanFactory,则销毁所有bean并关闭BeanFactory
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
// 实例化一个新的BeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
// 设置序列化id为唯一id
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
// BeanFactory的自定义配置
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 加载BeanDefinitions
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() {
return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory());
}
默认创建的BeanFactory就是DefaultListableBeanFactory对象。
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 设置classLoader(用于加载bean)
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
// 设置表达式解析器StandardBeanExpressionResolver(解析bean定义中的一些表达式)
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
// 添加属性编辑注册器(注册属性编辑器)
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// 添加ApplicationContextAwareProcessor这个BeanPostProcessor,保存在beanFactory的beanPostProcessors列表中
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
/**
* 取消
* EnvironmentAware,
* EmbeddedValueResolverAware,
* ResourceLoaderAware,
* ApplicationEventPublisherAware,
* MessageSourceAware,
* ApplicationContextAware这6个接口的自动注入。
* 因为ApplicatioinContextAwareProcessor把这6这个接口的实现工作做了。
*
*/
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
/**
* 设置特殊类型对应的bean。
* beanFactory对应刚刚获取的BeanFactory
* ResourceLoader, ApplicationEventPublisher, ApplicationContext这3个接口对应的bean都设置为当前的Spring容器。
*
* 保存在beanFactory的resolvableDependencies(ConcurrentHashMap)中。
*/
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// 注册ApplicationListenerDetector,用于发现实现了ApplicationListener接口的bean
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// 检查代码织入
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
/**
* 注册默认的environment, systemProperties, systemEnvironment
* 保存在beanFactory的singletonObjects(ConcurrentHashMap)、registeredSingletons(LinkedHashSet)、manualSingletonNames(LinkedHashSet)中
*/
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
==ApplicationContextAwareProcessor作为BeanPostProcessor的实现,在这里添加。==
PostProcessor相关
PostProcessor作用是注册和执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor,相关的介绍见:《BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor》。
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory)
在初始化BeanFactory后,提供给子类一个修改标准BeanFactory的扩展点(例如添加子类ApplicationContext需要的BeanPostProcessor)。
//ResourceAdapterApplicationContext中override的postProcessBeanFactory()方法:
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BootstrapContextAwareProcessor(this.bootstrapContext));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(BootstrapContextAware.class);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BootstrapContext.class, this.bootstrapContext);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(WorkManager.class, new ObjectFactory<WorkManager>() {
public WorkManager getObject() {
return ResourceAdapterApplicationContext.this.bootstrapContext.getWorkManager();
}
});
}
在ClassPathXmlApplicationContext中并未重写该方法。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, this.getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean("loadTimeWeaver")) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
this.getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()
获取所有在config中注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, this.getBeanFactoryPostProcessors())
源代码见:invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
-
判断BeanFactory是否实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry。
实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry的BeanFactory能够对BeanFactory中的BeanDefinitions进行添加、删除操作。(DefaultListableBeanFactory, GenericApplicationContext)。
-
如果实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry,则先找到并处理BeanFactoryPostProcessor中的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor。
/** * Extension to the standard {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} SPI, allowing for * the registration of further bean definitions <i>before</i> regular * BeanFactoryPostProcessor detection kicks in. In particular, * BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor may register further bean definitions * which in turn define BeanFactoryPostProcessor instances. */BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类,能够向BeanFactory中手动注册更多的BeanDefinition,包括BeanFactoryPostProcessor。BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor在其余BeanFactoryPostProcessor前处理,因此其新注册的BeanDefinition也能被后面的BeanFactoryPostProcessor处理。
-
处理完BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor后,再处理其余的BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
/** * Allows for custom modification of an application context's bean definitions, * adapting the bean property values of the context's underlying bean factory. * * <p>Application contexts can auto-detect BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans in * their bean definitions and apply them before any other beans get created. */BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(…)执行时,所有的BeanDefinition都被载入(包括BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor载入的),但还没有Bean被初始化。BeanFactoryPostProcessor能够在Bean初始化前对Bean Definition进行修改。
-
不管是处理BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor还是BeanFactoryPostProcessor,都需要按照定义的优先级顺序。
首先按定义的优先级顺序处理实现了PriorityOrdered接口的Processor。 再按定义的优先级顺序处理实现了Ordered接口的Processor。 再处理剩余的Processor。
由于Spring中大量的使用了策略模式,多个策略同时存在时需要区分调用顺序,因此提供了Ordered接口。PriorityOrdered继承了Ordered接口,并定义实现了PriorityOrdered接口的策略优先级高于Ordered接口。
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)
源代码registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)
按照PriorityOrdered和Ordered的顺序,将所有的BeanPostProcessor注册到BeanFactory。
BeanPostProcessor只有在Bean初始化的时候才会被调用,因此,在这里只是注册,不会被调用。
MessageSource, Event, Listener和其余工作
- 初始化 MessageSource bean,支持i18n多国语。
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
- 初始化EventMulticaster
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
ApplicationEventMulticaster定义了一个管理所有ApplicationListener的接口。如果用户提供了ApplicationEventMulticaster的实现bean则使用该实现,如果用户没有提供,则默认创建SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster。
- onRefresh()
提供给子类重写的函数,添加当refresh时,context相关的其他操作。
- 注册Listeners
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
将用户提供的ApplicationListener bean 注册到EventMulticaster。
结束refresh
- finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)
主要调用BeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons()
在finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)中初始化Bean以及调用Bean的初始化方法等,详见《Bean的生命周期管理及扩展点》。
- ==实例化==所有的non-lazy-init singleton Bean。
- ==调用所有实现InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet()方法==。
- ==调用BeanPostProcessors相关处理==。
- finishRefresh()
结束初始化工作。
- 初始化LifeCycleProcessor Bean。
- public ContextRefreshedEvent。
REFS
- https://my.oschina.net/u/2377110/blog/1023521
- http://www.cnblogs.com/ITtangtang/p/3978349.html
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/d75faa3ddce3
- https://www.cnblogs.com/xrq730/p/6285358.html
- http://www.cnblogs.com/question-sky/p/6760811.html
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/fca013ec1764
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/0e7f65afa156
- https://blog.csdn.net/caihaijiang/article/details/35552859 事件发布
- http://cxis.me/2017/02/15/Spring-ApplicationContext%E4%BA%8B%E4%BB%B6%E6%9C%BA%E5%88%B6/ GetBean
- https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000012887776
本文地址:https://cheng-dp.github.io/2019/03/05/application-context-basic-implement/